Introduction
Merge sort is a kind of a divide and conquest technique. Unlike Heap Sort, where we employ heap data structure to sort the array, for Merger Sort, we recursively bisect the input array to smaller subarrays, sort them and then recombine the subarray. This post will elaborates the technique to implement Merger Sort.
Concepts
Merger Sort follows the divide and conquest technique. The algorithm includes 3 basic steps:
- Divide the given unsorted list into several sublists, (Divide)
- Sort each of the sublist recursively. (Conquer)
- Merge the sorted sublist to produce new sorted list. (Combine)
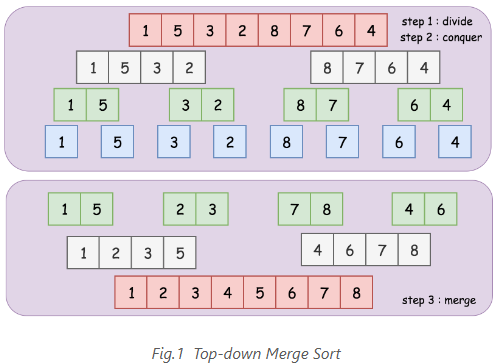
- Time Complexity:
O(nlogn) - Space Complexity:
O(1)
Implementation
There are slightly different techniques to implement the algorithm. Generally, We don't have 3 functions for 3 steps, but 2 functions and share the work in each step. We have 2 main functions: mergeSort and merge.
mergeSortis the initial call and performs step 1, step 2.- partition the input array into left and right subarrays of equal size.
- recursively calls itself to partition the subarrays until there is only 1 element (base case).
mergeperforms step 2 and 3, combining sorted subarrays.- When combining the subarrays, it compare each items of the left and right subarray.
- Smaller items from either arrays are filled first, then remaining item from left array, and then right array are filled.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Sort and Merges two subarrays of vec.
void merge(vector<int>& parentVect, vector<int>& left, vector<int>& right) {
int parentIndex = 0, leftIndex = 0, rightIndex = 0;
int leftBound = left.size();
int rightBound = right.size();
// Merge the two subarrays
while (leftIndex < leftBound && rightIndex < rightBound) {
if (left[leftIndex] <= right[rightIndex]) {
parentVect[parentIndex] = left[leftIndex];
leftIndex++;
} else {
// Ig: [5,4] [1,7] => L=[5,4] move right index, R=[7], parent=[1]
parentVect[parentIndex] = right[rightIndex];
rightIndex++;
}
parentIndex++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of left[], if any
while (leftIndex < leftBound) {
parentVect[parentIndex] = left[leftIndex];
parentIndex++;
leftIndex++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of right[], if any
while (rightIndex < rightBound) {
parentVect[parentIndex] = right[rightIndex];
parentIndex++;
rightIndex++;
}
}
// Divide the input arrays to subarrays until size = 1
void mergeSort(vector<int>& parentVect) {
if (parentVect.size() <= 1)
return;
int leftSize = parentVect.size() / 2;
int rightSize = parentVect.size() - leftSize;
// Create temporary vectors
vector<int> leftVect(leftSize), rightVect(rightSize);
// Copy data to temporary vectors
for (int i = 0; i < parentVect.size(); i++) {
if (i < leftSize)
leftVect[i] = parentVect[i];
else
rightVect[i - leftSize] = parentVect[i];
}
// Recursively break up the arrays
mergeSort(leftVect);
mergeSort(rightVect);
// Merge the sorted halves
merge(parentVect, leftVect, rightVect);
}
int main() {
vector<int> vec = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7};
// Sorting vec using mergesort
mergeSort(vec);
for (auto i : vec)
cout << i << " ";
return 0;
}