Introduction
In earlier blog, I discussed about 3GPP NG-RAN architecture. NG-RAN includes the 5G Core and 5G RAN. Interfaces such as Xn, X1, F1, E1 are briefly summarized.
O-RAN, as described on their page, is O-RAN ALLIANCE is a world-wide community of mobile operators, vendors, and research & academic institutions with the mission to re-shape Radio Access Networks to be more intelligent, open, virtualized and fully interoperable.
The O-RAN architecture adds several nodes, and interfaces to 3GPP 5G architecture to realize the above visions and goals. Yet, "the O-RAN architecture and interface specifications shall be consistent with 3GPP architecture and interface specifications to the extent possible".
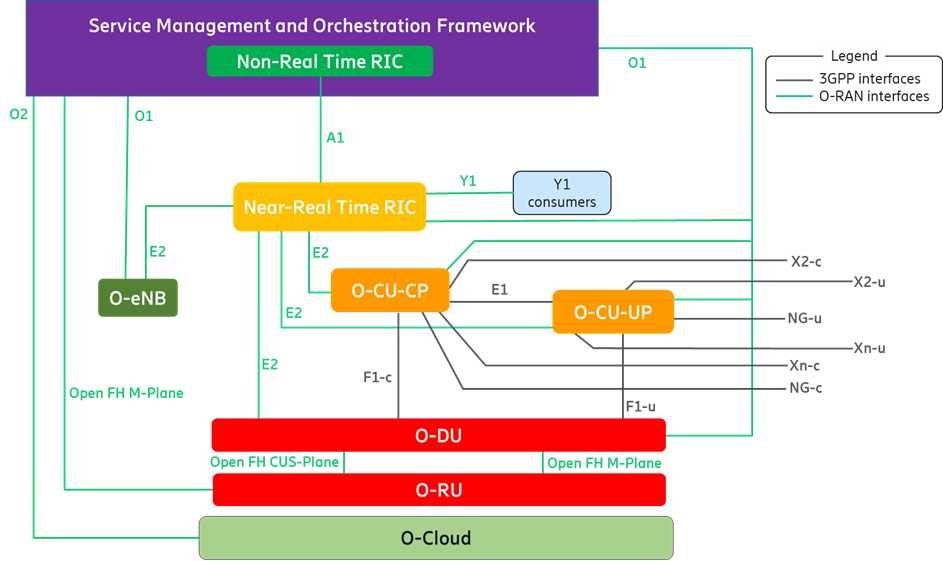
The following logical functions are added:
- Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) which includes Non Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller (Non-RT-RIC)
- O-RAN network functions, which includes Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller (Near-RT RIC), O-RAN Central Unit (O-CU), O-RAN Distributed Unit (O-DU).
- O-Cloud which is a cloud computing platform comprising a collection of physical infrastructure nodes that meet O-RAN requirements to host the relevant O-RAN functions.
Additionally, we have the following O-RAN interfaces:
- O1 interface between SMO and O-CU, O-DU,
- O2 interface between SMO and O-Cloud
- A1 interface Non-RT-RIC and the Near-RT RIC functions
- Open Fronthaul interface between O-DU and O-RU
- Open Fronthaul M-plane interface between SMO and O-RU
- E2 interface
- Y1 interface
- O-Cloud Notification interface
Commanding document is on O-RAN specification page. The document name is O-RAN.WG1.OAD-R003-v09.00
O-RAN specifications are already concise and should be used as main reference. This blog will not summarize the well-written documents. Instead, I will focus on some entities and interfaces within the O-RAN architecture and provide the reference to the O-RAN specifications.
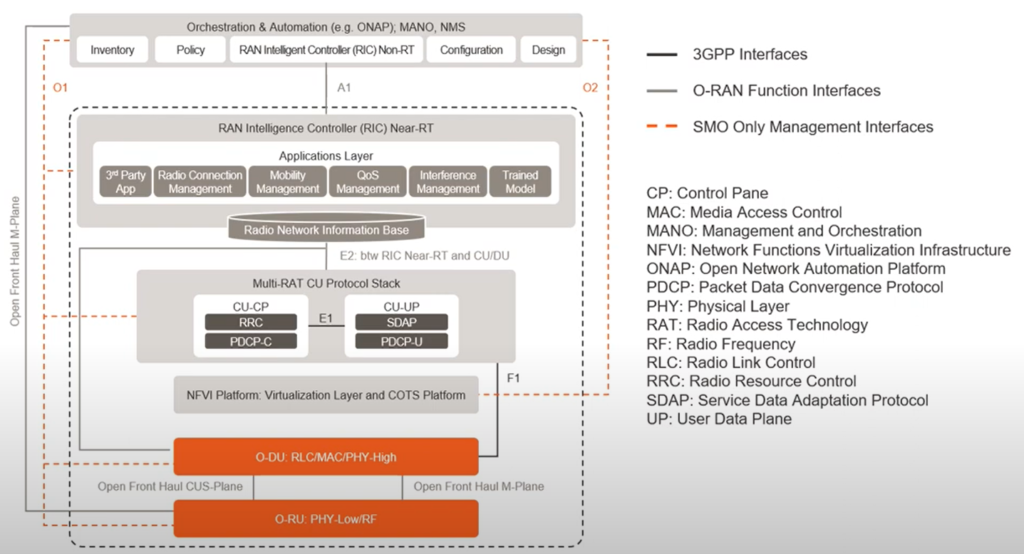
O-RAN Architecture
In this section, I briefly summarize the O-RAN logical nodes; the responsibilities and the interfaces between them in O-RAN are to be highlighted.
The following diagram details responsibilities, protocol stack splits between different O-RAN identities
Service Management and Orchestration
SMO is responsible for
- RAN domain management including fault, configuration, accounting, performance, and security (FCAPS).
- It includes Non-RT RIC for RAN Optimization using ML/AI.
- O-Cloud management
The following interfaces supports SMO management over O-CU, O-DU, O-RU and O-eNB functions:
- O1 interface supports the management of O-CU, O-DU and O-eNB.
- The Open Fronthaul M-plane interface, SMO <->O-RU, supports management of RU from SMO.
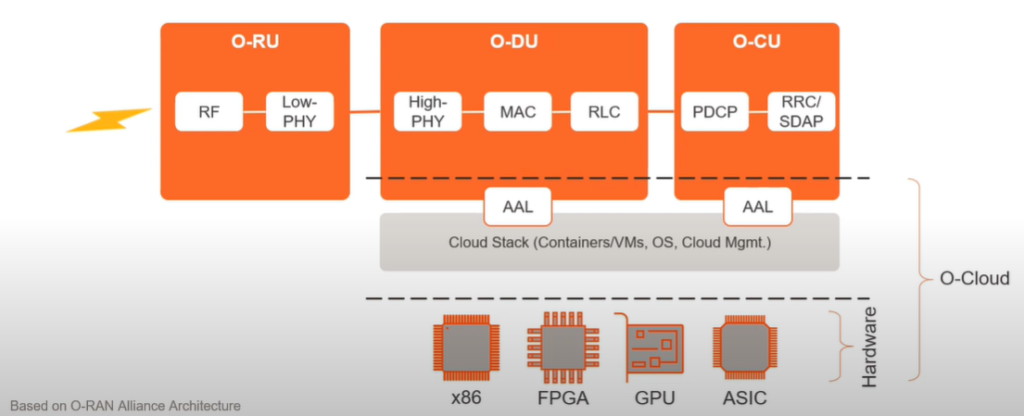
Open-RAN Centralized Unit, Distributed Unit and Radio Unit
- Open RAN Centralized Unit (O-CU) is a logical node hosting RRC/PDCP/SDAP based on a lower layer functional split.
- Open RAN Distribution Unit (O-DU) is a logical node hosting RLC/MAC/High-PHY layers based on a lower layer functional split.
- Open RAN Radio Unit (O-RU) is a logical node hosting a Low-PHY layer and RF processing based on a lower layer functional split.
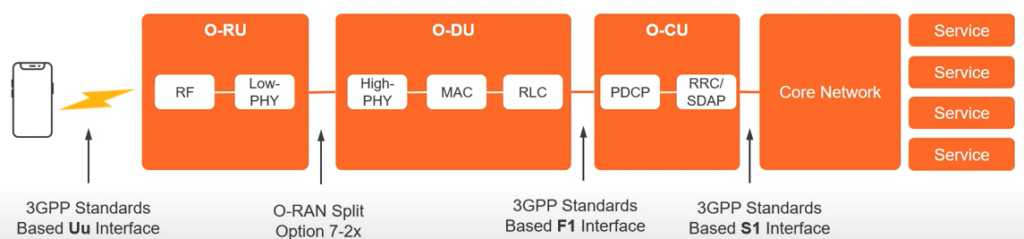
The following interface defines the connection between O-DU and O-RU:
- Open Fron Haul Interface defines the control messages, user data messages, synchronization messages in respective protocols.
- Open Fronthaul M-Plane interface defines FCAP functions that allow management of O-RU from SMO or O-DU in respective protocols.
Non-Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller
to be added
Near-Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller
to be added
O-Cloud:
O-Cloud is a cloud computing platform comprising a collection of physical infrastructure nodes that meet O-RAN requirements to host the relevant O-RAN functions. It would have 3 layers:
- Virtualized RAN software functions, that perform as O-DU or O-CU.
- Cloud stack functions.
- Hardware.
O-RAN CUSM plane
CUSM planes include SMO, O-DU, O-RU and the interfaces between them. The following diagram summarized the CUSM plane as below:
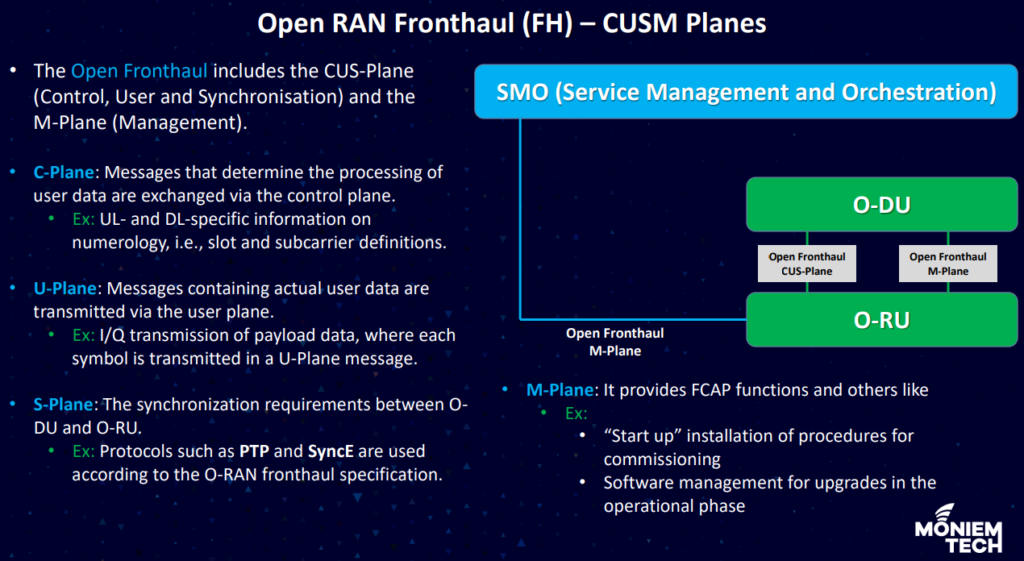
The CUSM plane are split into C-Plane, S-Plane, U-Plane and M-Plane. Each of which includes protocol stack as below:
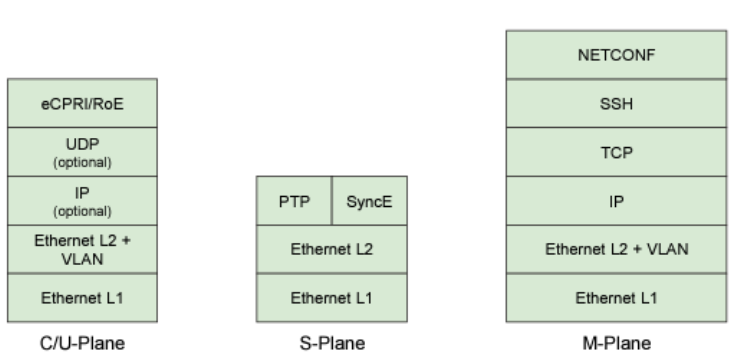
- eCPRI: enhanced Common Public Radio Interface is the protocol that is replacing the CPRI protocol in 5G to reduce the bandwidth BW requirements of CPRI transport and making Fronthaul affordable and available for all mobile network operators.
- NETCONF: Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) is a network management protocol developed and standardized by the IEFT. O-RAN Security Protocol requires NETCONF to be carried out by SSH.
- PTP:
- SyncE:
References
- O-RAN TS: O-RAN Architecture Description
- O-RAN TS: "Management Plane Specification"
- O-RAN TS: "Control, User and Synchronization Plane Specification"
- An Overview of O-RAN Architecture • Parallel Wireless
- What are C/U/M/S Fronthaul (FH) Planes in ORAN ? - Moniem-Tech
- What is The M-Plane in Open RAN? - Moniem-Tech