Introduction
UE has to received information for gNB to know how to connect to the site. gNB sends basic information such as Cell ID, frequency, time slot, decoding information in signals where UE can look for messages that contains further instruction. Certain events will trigger different types of information being sent to UE.
In this blog I attempt to summarize signals and messages to clear up confusion and hopefully serves as "cheat sheet" for quick remind. I will only explain:
- the signal and message's content, purposes
- where the message be on 5G frame, channels, or when they are sent
- but not include details various message content difference, or message' s configuration.
I will explain the signal and messages in order of the following UE attach procedures:
- Downlink Synchronization process
- Uplink Synchronization (RACH process)
- RRC Connection Establishment
In addition, I also briefly describe messages between UE and gNB that are involved in Paging process, and Handover process
To understand this page, it is vital to have basic understand of 5G Frame structure. I have a blog post here.
Downlink Synchronization Process
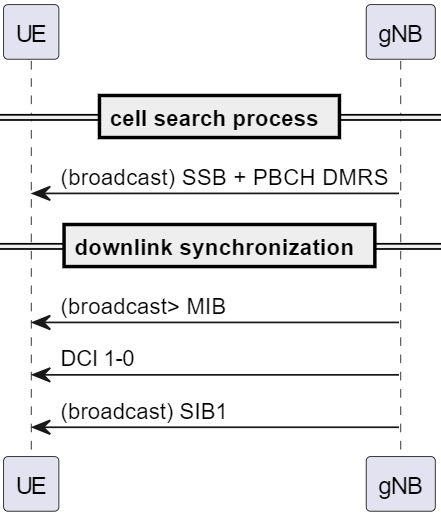
SSB (Synchronization Signal Block)
- 3GPP resource: 38.300-5.2.4
- Use for downlink synchronization, cell search, and initial beamforming
- PSS (Primary Synchronization Sequence) provides timing estimate
- SSS (Secondary Synchronization Sequence) provides Physical Cell ID
- DMRS (Demodulation Reference Signal for PBCH): tells UE bout channel estimation for demodulate PBCH and reads MIB.
- MIB (Master Information Block): contains information such as SIB1's numerology, DCI 1_0 (configuration and decoding information for SIB1), system frame number, Frequency Offset between SS Block and common resource grid, time domain position of 1st DM-RS signal Type A, or PDSCH DMRS, cell baring info
- Based on
MIB.pdcch-ConfigSIB1, UE will find the location of CORESET0 and SearchSpace information. Then decode DCI 1_0.
- Based on
MIB ::= SEQUENCE {
systemFrameNumber BIT STRING (SIZE (6)), => 6 bits
subCarrierSpacingCommon ENUMERATED {scs15or60, scs30or120}, => 1 bit
ssb-SubcarrierOffset INTEGER (0..15), => 4 bits
dmrs-TypeA-Position ENUMERATED {pos2, pos3}, => 1 bit
pdcch-ConfigSIB1 INTEGER (0..255), => 8 bits
cellBarred ENUMERATED {barred, notBarred}, => 1 bit
intraFreqReselection ENUMERATED {allowed, notAllowed}, => 1 bit
spare BIT STRING (SIZE (1)) => 1 bit
}- SSB are transmitted in at exact domain and in certain pattern (time burses).
DMRS (Demodulation Reference Signal)
- tell UE about channel estimation of associated physical channels. Thus we have DMRS on PBCH, DMRS for PDSCH, DMRS for PUSCH.
DCI (Downlink Control Information)
Master Information Block (MIB) on PBCH provides the UE with parameters (e.g. CORESET#0 configuration) for monitoring of PDCCH for scheduling PDSCH that carries the System Information Block 1 (SIB1)
- DCI includes Frequency and Time Resource allocation information, modulation, coding scheme, antenna ports, HARQ information, and number of spatial layers for UE.
- Different DCI format carries different information
DCI 1_0carries scheduling information for SIB messages on PDSCHDCI 1_1carries scheduling information for messages on PDSCH such as RAR, RRCDCI 0_0orDCI 1_0carries scheduling information for Msg4 (RRCSetupRequest)
- DCI is transmitted in frequency domain within CORESET. A CORESET is made up of multiples resource blocks (i.e, multiples of 12 REs) in frequency domain and '1 or 2 or 3' OFDM symbols in time domain
Reference: CORESET0 and SIB1: 5G | ShareTechnote
SIB (System Information Block)
SIB1message is an RRC message that contains "Remaining Minimum System Information" such as. PLMN ID, cell selection parameters, RACH parameters.SIB1is transmitted periodically (160ms), but other SIB may be requested by UE. Source: 38.331-5.2.1- Generally, all SIBs are RRC messages (L3). They include:
servingCellConfigCommonServingCellConfigCommonSIB: this information tell UE about SSB tranmission patternDownlinkConfigCommonSIB: config for bcch, pcch (paging channel)PDCCH-ConfigCommon: config for dedicated downlink (carry user data) channelRACH-ConfigCommon: config info for SSB.RACH-ConfigGeneric: config info for RAR such when how long gNB may send back RAR- and others info.
- They are transmitted on CCCH or DCCH (logical channel) and mapped to DL-SCH (transport channel).
- SRB (Radio Resource Bearer) carries SIB messages.
Excerpt of RACH configuration info from SIB1:
RACH-ConfigGeneric ::= SEQUENCE {
prach-ConfigurationIndex INTEGER (0..255),
msg1-FDM ENUMERATED {one, two, four, eight},
msg1-FrequencyStart INTEGER (0..maxNrofPhysicalResourceBlocks-1),
zeroCorrelationZoneConfig INTEGER(0..15),
preambleReceivedTargetPower INTEGER (-200..-74),
preambleTransMax ENUMERATED {n3,n4,n5,n6,n7,n8,n10,n20,n50,n100,n200},
powerRampingStep ENUMERATED {dB0, dB2, dB4, dB6},
ra-ResponseWindow ENUMERATED {sl1, sl2, sl4, sl8, sl10, sl20, sl40, sl80}
}Uplink synchronization process
UL synchronization process includes the UE sending Preamble, and receives UL grant, which allows UE to gain time and frequency resource allocation on UL channel.
3GPP resource: 38.321 - 5.1
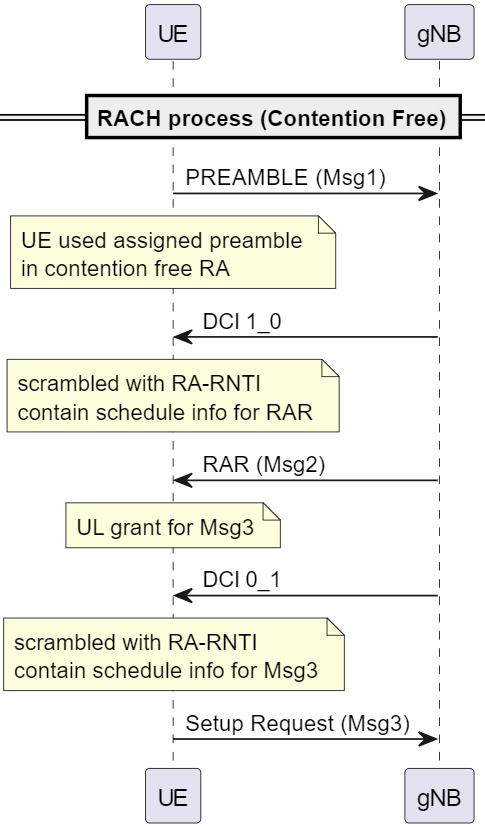
Preamble
- UE send preamble codes that it randomly constructed from PSS and SSS to gNB to request connection.
- the codes are sent on PRACH channel.
RAR ( Random Access Response)
- assigns UE identity and give UL grant for UE to send the next message.
- RAR message contents:
- Temporary Cell-RNTI
- RAR grant or UL grant so that UE can send Msg4 RRCSetupRequest. The info includes scheduling informations for frequency hopping, frequency and time domain reqsource allocation, MCS, and transmit power control
- gNB sends
RARon DL-SCH.
RRC Setup Request
- UE sends
RRCSetupRequestto request connection after it receivesRAR. - RRCSetupRequest contents:
- UE identity
- establishmentClause
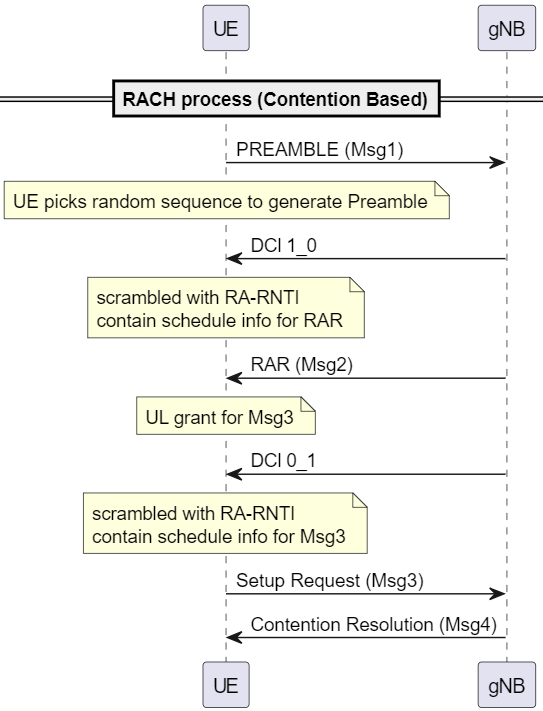
Contention Resolution (Msg 4)
2 UE may have sent the same Preambles, and may have received the same info for UL grant. Thus, the UEs, send RRC setup request to gNB on the same channel, same freq, and same time. 2 scenarios happens:
- the messages from UE interfere with each other and gNB couldn't decode. Thus both UE will not be able to connect to network and has to retry the process.
- one message is successfully decoded by the gNB, and gNB will connect that UE.
Registration Process - Authentication process
After RRC Request Message or Contention Resolution is sent from gNB to UE, UE will reply with RRC Setup Response and a NAS resgistration request.
This message initiates the following process:
- Authentication Process: The AMF generates an authentication challenge for the UE, which includes a random number and an expected authentication response. The UE computes the authentication response based on the challenge and its security credentials, and sends it back to the AMF. If the response matches the expected value, the authentication is successful
- Security Process: the UE and network establish security keys for secure communication. The AMF sends a
Security Mode Commandto the UE, specifying the security algorithms to be used for ciphering and integrity protection. The UE acknowledges the command with aSecurity Mode Completemessage - Registration Process: AMF sends a Registration Accept message to the UE, which includes the UE's 5G-GUTI (Globally Unique Temporary Identifier) and other relevant configuration information. The UE is now successfully registered with the 5G network
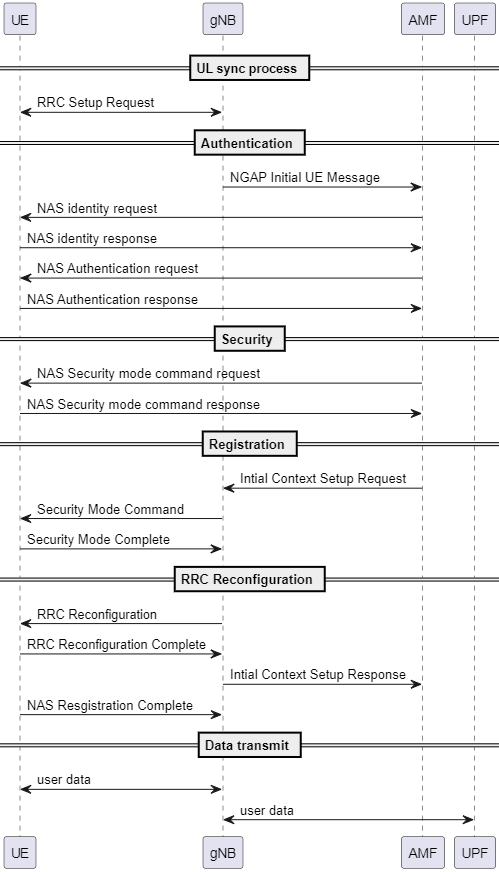
Connection control - RRC Establishment process
3GPP Resource: 38.331 - 5.3
RRC Reconfiguration
RRC Reconfigurationare messages that:- could establish/remodify/release Radio Bearer (both SRB and DRB)
- could establish/modify/release
- include site configuration: bandwidth part, cell ID, subscarrier spacing, DMRS positions, DL/UL config,
- include information for paging, sib etc...
- MeasConfig: instruct UE to make network measurement such as power.
RRC Reconfigurationis sent on DL-SCHRRC Reconfigurationis sent when:- establish first time connection.
- performing H/O if measurement report from UE shows that connection to current cell is weak.
Paging process (gNB wakes UE up)
3GPP resource: 38.331-5.3.2 ,(paging) and 38.331-5.3.13 (RRC Resume)
Paging procedure wakes up UE from idle mode. The UE stays in idle mode for certain period of time (DRX cycle), and wake up to listen to paging message. The UE then looks for its identity in Paging record.
If it founds its identity, then UE immediately send RRC Setup Request. (no RACH procedure is followed).
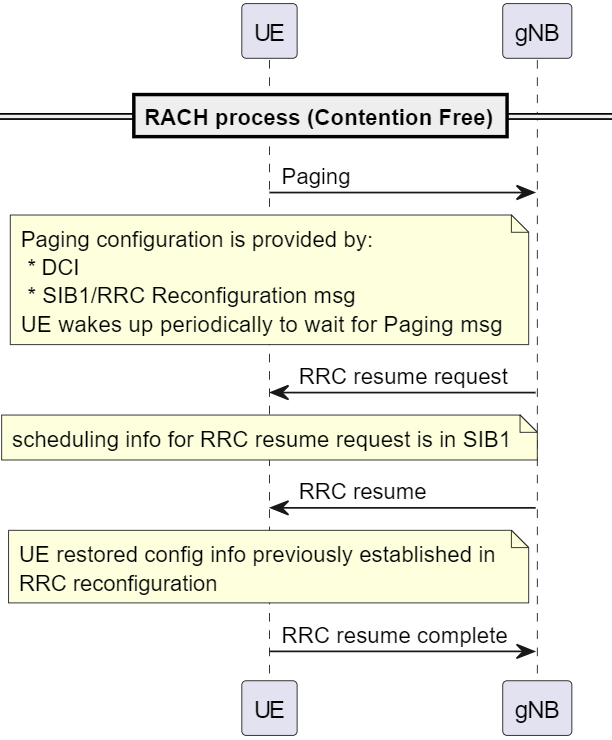
Paging
- gNB
Pagingnotifies UE to wake up from idle to receive text messages or call or other system information messages. gNB could page all UEs or specific UE that it has record. - Paging config info may be included in SIB1. DCI 2-6 also includes DRX cycle info.
- Paging includes
- PagingRecord
- PagingUE-Identity
- Paging is sent on PCH channel
DCI 1_0includes Short Message Indicator bits that tells UE of Paging scheduling (Paging period or DRX cycle) => UE wake up periodically to listen to Paging message. Resource: 38.212 Table 7.3.1.2.1-1
Handover process
Handover process is considered start with measurement report, after which the Source gNB makes handover decision.

Measurement Report
- measurement report is configured by RRC Reconfiguration message.
Reconnection process
RRC Connection Reestablishment
RRC Connection Reestablishment requestis sent by UE to request reestablishment. It requests to reestablish SRB0 => after this message is received by gNB, SIB1 should be sent to UE.- it includes:
- ue-Identity
- reestablishmentCause
- It is sent when: (38.331 section 5.3.7.2)
- UE detect radio link failure
- H/O failure occure
- RRC Reconfiguration was sent to UE but UE cannot perform success configuration.