Introduction
I attempt this series of blog posts to review knowledge of 5G network. There are quite a number of blogs and materials that should be used as reference. Sharetechnote and Eventhelis are my favorite. They have enough details for work reference, yet summarizes the technology quite understandable. Of course 3GPP specification should always be used as commanding document.
This blog post attempt to summarize the bare minimum knowledge. I give an overview of all protocols and proceed to explain RRC and MAC in slight details. Consider it as a cheat sheet, scram notes. I attempt to summarize the knowledge and at the same time give reference to 3GPP document, Sharetechnote or other useful pages.
Protocol Stacks
Protocols used in 5G networks depends on the "plane. There are User Plane and Control Plane in 5G.
- User Plane: includes channels and protocols that are responsible for the transmission of user data between connected devices and applications
- Control Plane: includes channels and protocols that are responsible for managing and controlling various aspects of the network
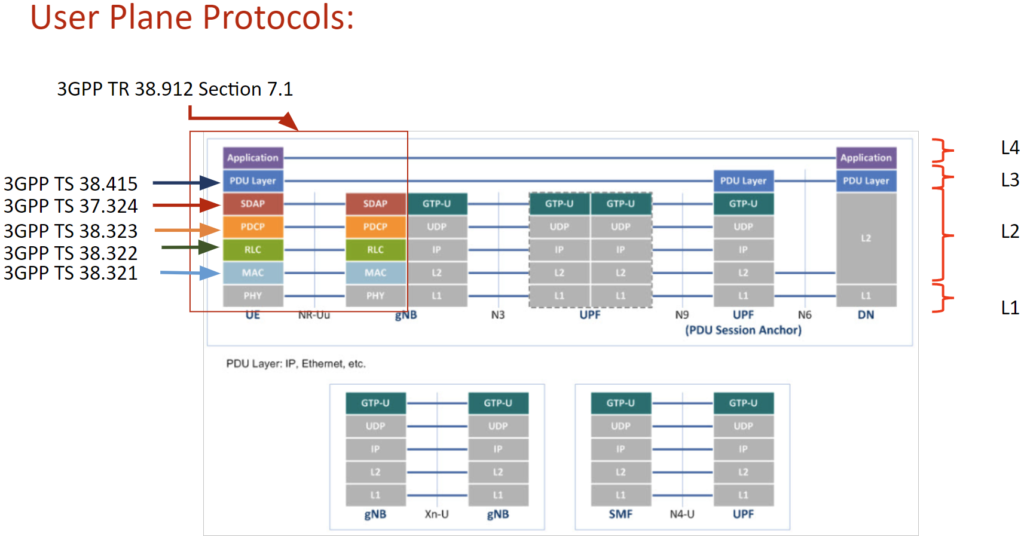
The following diagram illustrate protocol stacks used in 5G network control plane:

The following are network nodes (network elements) in control plane.
- UEs are User Equipment
- gNB: the base station that transmit signals to UE and receives data the from core network. For control plane, only the AMF and SMF part of the core network communicates with gNB
- AMF: Access and Mobility Management Function performs responsibilities such as access control (allowing UE to access network), mobility control (allow UE to travel to different gNB), etc.
- SMF: Session Management Function performs session management, quality of service, etc.
- UPF: User Plane Function. Its main functionality would be on User Plane, but it also communicates with SMF to facilitate its work responsibility.
The protocols are described in various 3GPP specifications as well as RFC as indicated on the diagram. Those protocols will be explained in later sections.
5G call flows
Protocols responsibility can't be well understood if UE call flow are not discussed before hand. Call flows are the flows of messages and respective information that are transmitted between UE and gNB as well as between gNB and Core network.
This particular EventHelix page has a great diagram to illustrate UE initial access call flow. The starting point however starts with Msg1 from UE, the Preamble.
Sharetechnote page explains the flows starting with Downlink Synchronization steps where gNB sends site information to UE via an RRC Reconfiguration msg or via SSB. Afterwhich, UE can initiates RACH process with its Preamble.
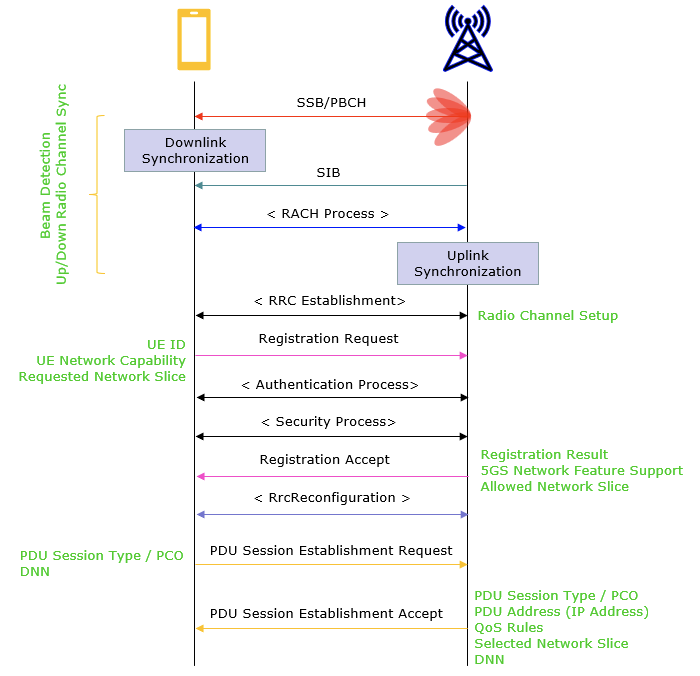
The following illustrates basic connections steps between UE and gNB.
- Step 0 Initiating Downlink Synchronization. SSB is sent on PBCH from gNB to UE that allows UE to collect site information. Furthermore, SIB are send to more details.
- Step 1 Sending Preamble. UE sends Preamble to gNB on PRACH physical channel
- Step 2 Random Access Response. gNB response with a DCI 1_0 signal and RAR message. DCI 1_0 helps UE decode RAR message on PDCCH channel
- Step 3 Initial Uplink Synchronization UE process
RAR messagesto adjust timing advance (align its time and frequency synchronization with gNB). UE also receive uplink grant (radio resource, or which frequency, PUSCH channel to transmit next message) - Step 4 RRC Connection Establishment.
RRCSetupRequestor Msg3 is sent by UE on PUSCH channel to request connection. It contains UE identity and establishment cause. - Step 5 RRC Connection Setup gNB sends
RRCSetupmessage with radio bearer config and cell infomation - Step 6 Registration and Authentication: NAS messages are sent between UE and gNB to authenticate UE to network.
- Step 7 Bearer Establishment.
RRCReconfigurationis sent to UE to set up Radio Bearer and UE confirms successful setup - Step 8 Data Transfer: uplink and downlink use data are sent
- Step 9 Call Termination
- Step10 Idle mode
5G channels
5G defines Physical, Transport and Logical channels. Corresponding protocol messages at certain layers are transmitted on those respective channels.
The following illustrates the channels and protocols
Protocol stacks at UE and gNB
Protocols dictates communication messages' format between 2 entities. All of my works are at gNB, thus I only have knowledge on those protocols, and can only cite some of them here.
RRC (Radio Resource Management - L3)
If you ever work as a drive tester, this would be the first protocol that you work with a lot. Drive Testers have to identify if the UE successfully connect to a gNB, switch between gNB or disconnect properly after a call. They will look at some basic RRC messages that indicates such events.
The following are some of the responsibility of RRC (details in TS.23.331 Section 4.4)
- Connection Establishment and Release: establishes connection after UE has successfully detects PREAMBLE, decodes DCI, performs authentication. a UE identity is assigned to the UE. Some RRC messages to be used are:
RRCConnect,RRCSetup,RRCReconfiguration - Idle Mode and Connected Mode: UE could go to idle mode if call is note made and awake at certain time, and listen to DCI signal to attempt next connection.
MIB and SIB messageprovides network information after UE awake from idle. - Mobility Management: UE provides signal measurement to gNB, which utilizes the information to instruct UE to handover to an adjacent site that has better signal. RRCReconfiguration, RRC Reestablisment messages may be used in such scenarios:
- Network Access Control: defines SIB message contain system information that support UE connections
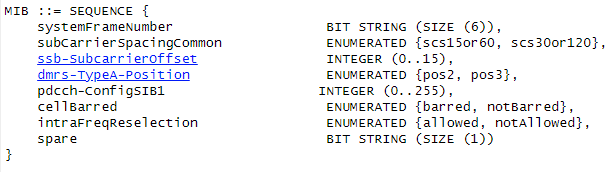
System Information (MIB or SIB)
System information messages transmitted on transport channels such as BCH (MIB message) and DL-SCH (SIBs). Those messages must be decoded before RRCSetup message could be sent by UE and further connection steps could be done.
Below is a sample of MIB information messages:
Signaling Radio Bearers
SRB are used only for the transmission of RRC (and NAS messages). They are signaling messages, and transmitted by logical channels. Refer to above channel and protocol diagram.
- SRB0 is for RRC messages using the CCCH channel
- SRB1 is for RRC messages using DCCH channel
- SRB2, SRB3 is for NAS and RRC messages on DCCH channel
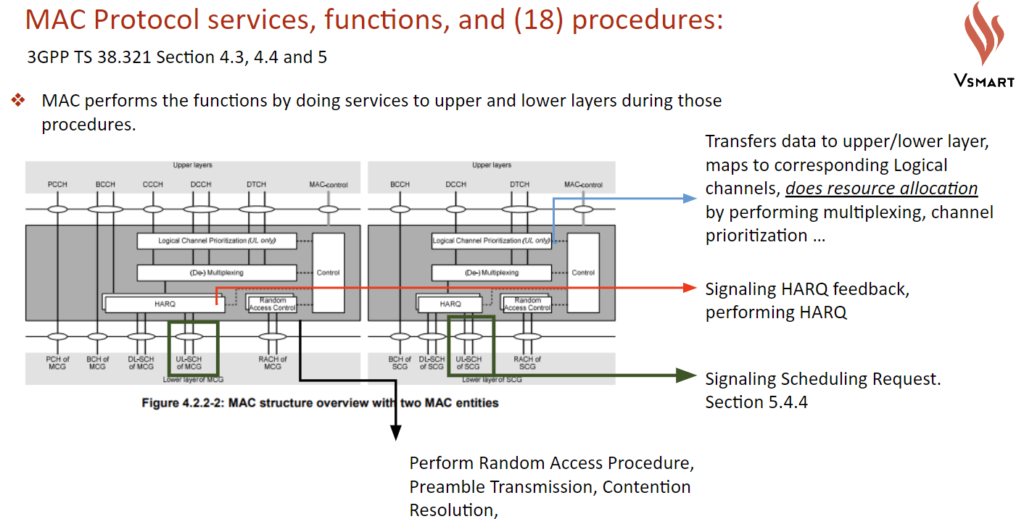
MAC (Medium Access Control - L2)
As the name implies, MAC plays important roles in initial access steps. Besides, MAC plays the following roles and more:
- Random Access: MAC manages PRACH channel which carries
SSB (System Information Block). MAC entity in UE initiates Random Access procedure. Preamble is sent from UE in Msg1. RAR is sent back from gNB in Msg2, which provides uplink grant to UE. UE use the resource to send Msg3RRCSetupRequest. - Error correction through HARQ: Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request is an error correction and retransmission scheme. Each HARQ process support one or two transport block.
- Multiplexing/Demultiplexing transport block to deliver to physical layer/transport layer.
- Mapping between transport channel and logical channel:
- Scheduling Request
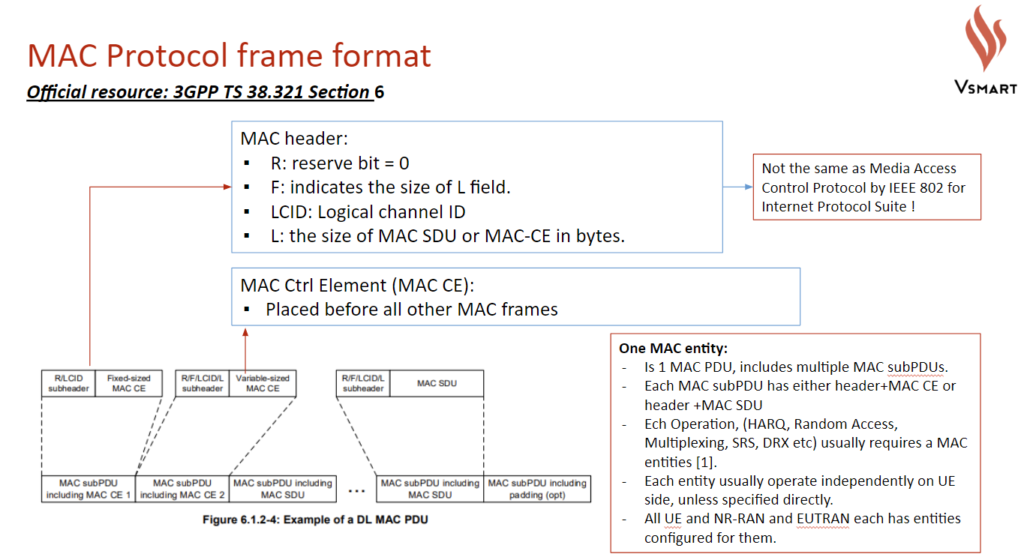
The following diagram on 3GPP 38.321 illustrate the work done by and corresponding channels used by MAC
MAC Random Access Procedure
2 types of RACH Process: Contention based and Non-Contention based
- Contention based: UE recieves all the information about Sync and RACH configuration from LTE RRC Connection Reconfiguration instead of MIB/SIB in NR. UE will send random Preamble, which may collide with other UE. Thus a contention resolution is needed later.
- Non-Contention based: gNB informs UE when and how to send Preamble and starts RACH process. RRC Reconfiguration message is sent from gNB to UE.
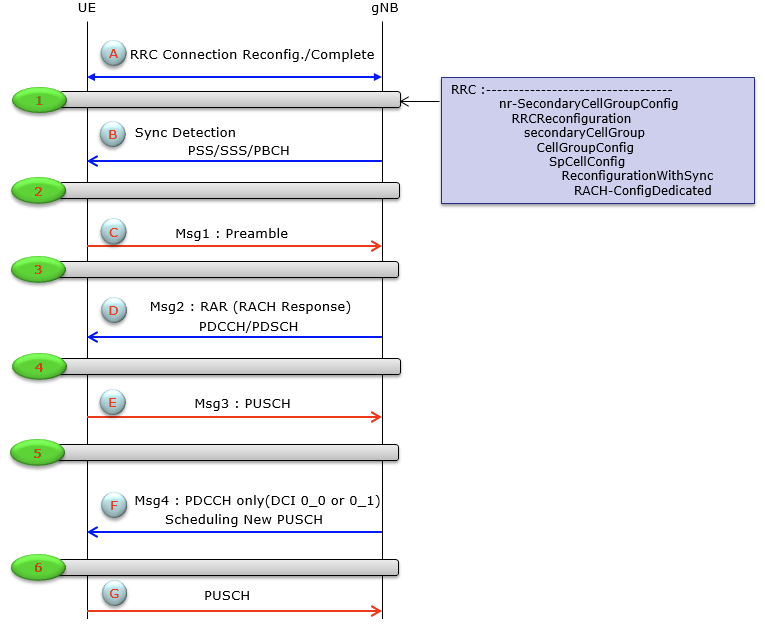
Contention Based RACH:
Contention Free RACH:
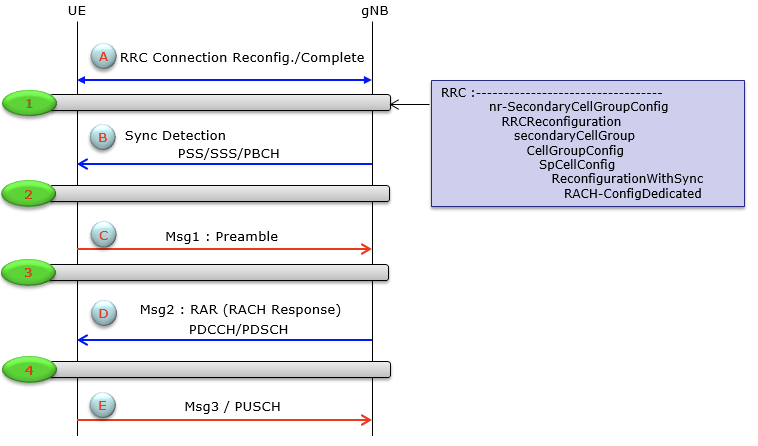
Initial Access could mean Downlink Synchronization + RACH process (Uplink Synchronization)
- Downlink Synchronization: PSS/SSS are sent on PBCH that includes information of radio frame boundary, subframe boundary, Physical cell ID, beamforming information.
- Uplink Synchronization (RACH): UE and gNB exchanges messages (Preamble and RAR) to achieve uplink sync between UE and gNB. UE also receives uplink grant (uplink radio resources) to send the next message. (RRCSetupRequest)
The following details the steps, messages and information exchanged between UE and gNB in RACH process.
- Step1.a: (if Contention based) RRC Reconfiguration message includes information to start RACH procedure
- Step1.b: (if Non-Contention based) gNB sends PSS/SSS, and DCI format, MIB, SIB on PDCCH. [Section 5.1.1]
- RRC Reconfiguration is sent on (DL-SCH->DCCH) on SRB3 [1]
- prach-ConfigurationIndex when UE can send Preamble and Preamble format
- Step2: gNB sends RA request (Preamble) [section 5.1.2 and 5.1.3]
- UE selects Delta-Preamble, set to MAC-CE.
- UE instructs PHY to implicitly transmit RA-RNTI.
- Step3: gNB sends RA response: [section 5.1.3
- includes Timing Advance Command in MAC-CE, send to UE. UE adjust its UL transmission
- Step4: gNB sends information to UE on RRC Reconfiguration msg via (DL-SCH -> DCCH) on SRB3 [1]
- Step5: eNB sends RRC Setup Request.
The following details a MAC frame:
Conclusion
There are more protocols that need to be discussed, but RRC and MAC were the two assigned to me as first researching task when I started my job at Vinsmart. I find them a very good starting point get good gasp of 5G fundamentals. After all, it is logical to know the first steps for User device and Network to make connection.
In the next blog post, I will discuss about 5G Function Split Options. Why? Because it is how DU/CU devices are made: each type of devices will perform certain tasks. In other words, certain protocol stacks stays on those devices.
Next, the DU and CU have to send messages to each other. This is also how the information is sent between protocol layers. When I was QA engineer at Vinsmart, I have to look at those messages to find out the information processed at each layer. Figuring out those information will reinforce our understand of the 5G protocol stacks.